Crude Oil Prices Slide as Economic Concerns and OPEC+ Decisions Weigh on Market
Weak demand from China and the US, combined with potential OPEC+ production delays, push oil prices to multi-month lows, raising concerns over global supply and demand dynamics | That's TradingNEWS
Crude Oil Markets Face Pressure Amid Recession Fears and Volatile Geopolitical Conditions
Weak Economic Data Fuels Oil Price Decline
Crude oil prices have faced significant pressure in recent weeks, as weak economic data from the US and China has eroded demand forecasts, contributing to an overall bearish market sentiment. Both major benchmarks, West Texas Intermediate (WTI) and Brent Crude, have seen sharp declines, with WTI dropping below $70 per barrel, marking its lowest level since December 2023. Brent has also slumped below $74 per barrel, its weakest price in nine months. This sharp drop has seen both futures decline more than 10% since late August, as investors retreat from riskier assets amid recession concerns.
Rising Fears of Global Economic Recession
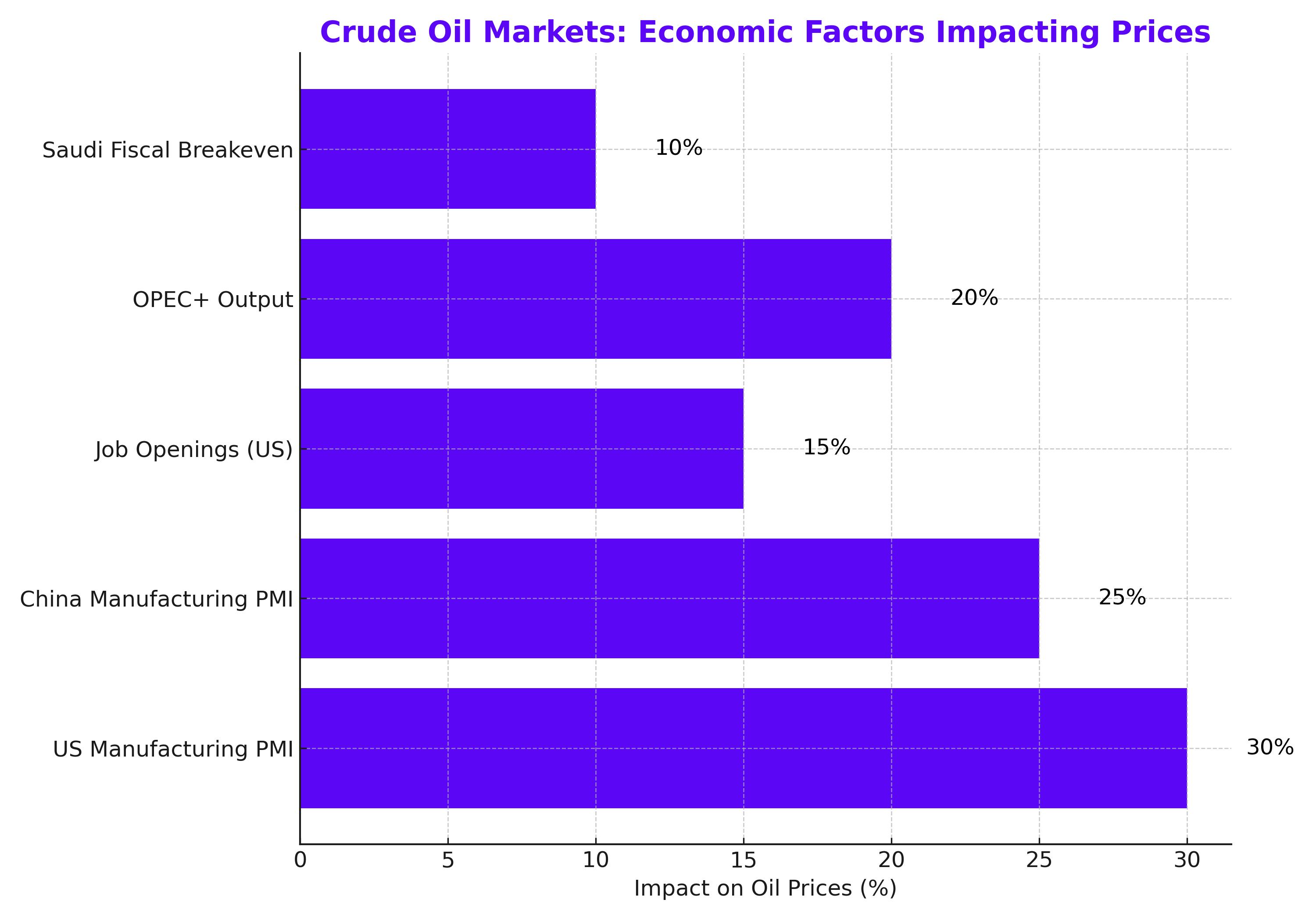
The global oil market's volatility is closely tied to concerns about a potential economic recession, particularly in the world’s largest economies. In the US, data revealed a weaker-than-expected Manufacturing Purchasing Manager Index (PMI) for August, signaling a contraction in industrial activity for the fourth straight month. Job openings in the US fell to their lowest point since January 2021, further dampening economic confidence. This weaker data has led to growing speculation that the Federal Reserve may implement a deeper rate cut next month. With two-year and ten-year Treasury yields briefly reversing inversion for the second time since 2022, investors remain cautious about the broader economic outlook.
Meanwhile, China's economic recovery has faltered, with weaker-than-expected Manufacturing PMI data indicating contraction for a third consecutive month. Additionally, the Caixin Services PMI, released on Wednesday, also showed disappointing results, reflecting the broader slowdown in China's post-pandemic recovery. As the largest global importer of oil, China’s sluggish demand significantly impacts global crude prices.
OPEC+ Faces Tough Decisions Amid Price Declines
Amid plummeting oil prices, OPEC+ members are reconsidering their plans to increase production in October. Initially, the group, led by Saudi Arabia and Russia, planned to raise output by 180,000 barrels per day. However, the sharp downturn in oil prices has forced the organization to reconsider. If these production cuts continue, the market may see some support, though analysts are cautious about how much impact this will have on the current bearish sentiment.
OPEC+ has implemented output cuts since 2022, and with current production reduced by over 5.86 million barrels per day, these cuts account for roughly 5.7% of global demand. Saudi Arabia, the group’s most influential member, plays a critical role, especially as it seeks to balance its fiscal needs with oil production. With its fiscal breakeven oil price for 2024 now projected at $96.20 per barrel, Saudi Arabia faces growing pressure as it navigates its Vision 2030 economic reforms, aimed at reducing the kingdom’s reliance on oil revenues.
Saudi Arabia’s Breakeven Challenges and Global Supply Uncertainties
Saudi Arabia, the world’s largest oil exporter, operates with one of the lowest production costs globally, averaging just $10 per barrel. However, with its ambitious Vision 2030 agenda, which involves massive infrastructure projects and investments, the kingdom's fiscal breakeven price has steadily risen. As of May 2023, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimated Saudi Arabia's breakeven price at $80.90 per barrel, but this has since climbed to $96.20 for 2024. This gap between market prices and the fiscal breakeven could lead to more conservative output policies from the kingdom to support higher oil prices.
Additionally, the rise of oil production from non-OPEC countries, such as the US, Brazil, and Guyana, adds further complexity to the market. The United States, for example, has expanded its shale oil production, contributing to oversupply concerns. Should this trend continue, OPEC+ may need to further delay its output increases to stabilize prices.
Supply Concerns and Market Volatility
Another factor influencing oil prices is ongoing uncertainty surrounding supply disruptions in key producing regions. In late August, oil prices surged due to escalating geopolitical tensions between Iran and Israel, as well as production halts in Libya. However, with the prospect of a resolution in Libya and a reduction in regional tensions, those price spikes have since reversed.
On the supply side, US oil inventories have shown significant declines, according to the American Petroleum Institute (API). The most recent data indicated that US crude inventories fell by 7.4 million barrels, far exceeding analysts' expectations of a 1.3 million barrel decline. While this figure provided some short-term support to oil prices, the overarching concerns about demand are likely to overshadow any immediate gains from lower inventories.
Future Outlook: Recession Risks and Demand Uncertainty
Looking ahead, oil markets remain poised between opposing forces. On the one hand, recession fears driven by weak economic data and ongoing rate hikes by central banks, including the Federal Reserve, suggest that demand for oil could weaken further. On the other hand, geopolitical factors and supply disruptions in key producing countries create volatility that could continue to drive short-term price fluctuations.
However, the long-term trajectory of oil prices is largely dependent on how OPEC+ responds to these challenges. If the group delays production increases or even extends current cuts into 2025, it could offer a degree of price support. Yet, given the significant economic uncertainties in major oil-consuming countries, particularly China and the US, oil markets are likely to remain under pressure in the coming months.
That's TradingNEWS
Read More
-
IVV ETF Price Forecast: Is $684 Still Worth Paying For S&P 500 Exposure?
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveStocks
-
XRP ETF Rally: XRPI at $8.09 and XRPR at $11.60 as XRP-USD Rebounds Toward $1.47
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCrypto
-
Natural Gas Futures Price Holds Around $3.20 as Storage Tightens and Winter Premium Fades
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCommodities
-
USD/JPY Price Forecast: Yen Strength Turns 152 into a Make-or-Break Level
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveForex