India Doubles Down on Russian Oil: A Game-Changing Energy Play in a Tightening Market
With OPEC+ cuts and rising global demand, India turns to Russian crude to fuel its growing energy needs, positioning itself as a key player in the shifting oil landscape | That's TradingNEWS
Oil Markets Overview: India’s Strategic Moves and Global Supply Dynamics
India's Role in the Global Oil Market: Driving Demand Growth
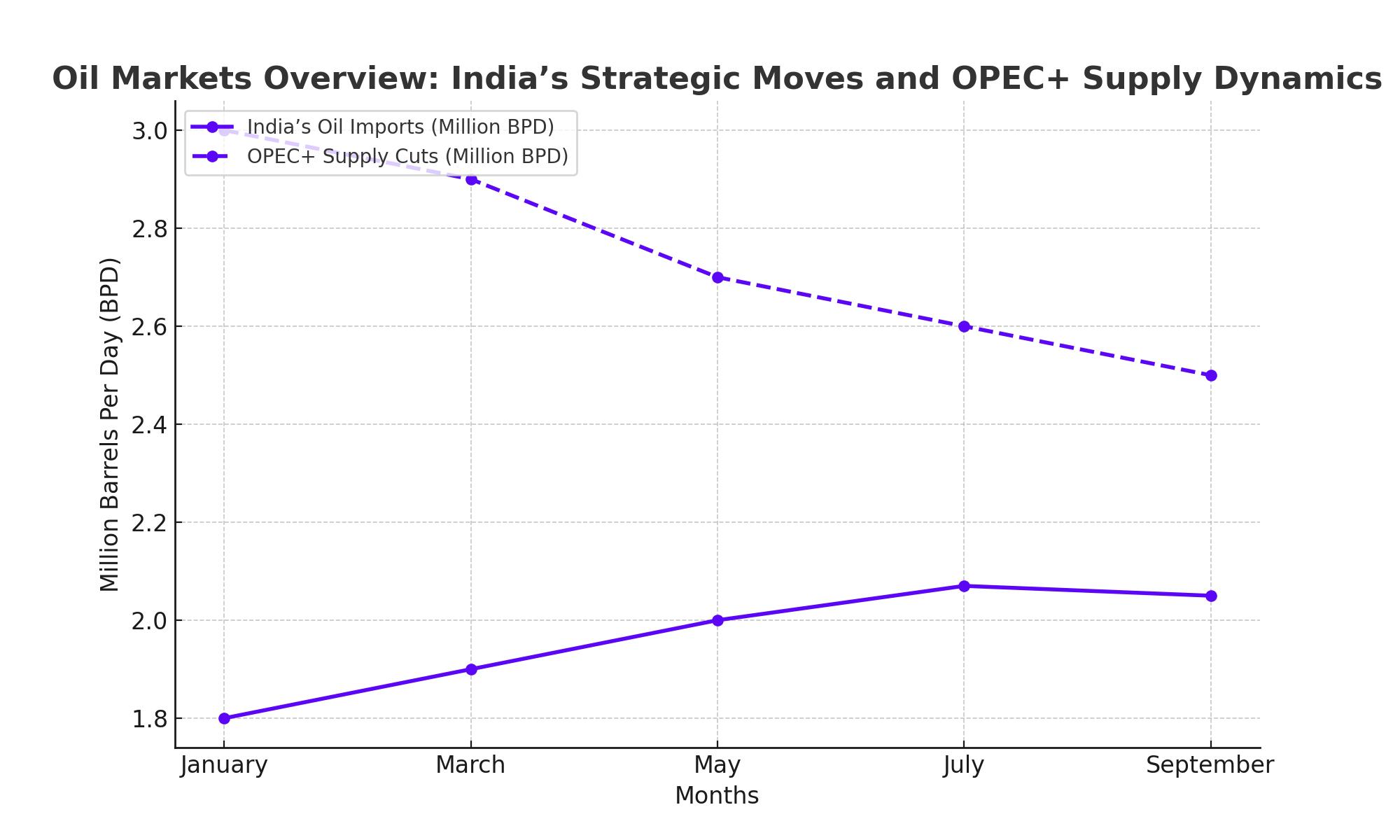
India, the world’s third-largest oil importer, plays a pivotal role in shaping global energy demand. The country imports over 85% of its petroleum needs, and this dependency is expected to grow as its economy expands. India’s reliance on discounted Russian crude has been instrumental in meeting its energy demands. With Russia offering oil at a discount due to Western sanctions, India has taken full advantage, becoming Russia’s largest oil customer. In July 2024, India surpassed China, importing a record 2.07 million barrels per day (bpd) from Russia—44% of India’s total crude imports.
Indian state-owned refiners are now in discussions for long-term supply agreements with Russia, seeking “predictable and stable” oil supplies as India aims to boost its refining capacity by 20% to 6.19 million bpd by 2028.
Global Oil Supply Constraints: Impact of OPEC+ and U.S. Production
Global oil markets remain tight, despite concerns over weak demand and fluctuating prices. The extended OPEC+ production cuts, led by major producers like Saudi Arabia and Russia, are expected to keep the supply constrained. In 2024, global crude oil supply is forecast to decline by 220,000 bpd due to these cuts and reduced Libyan output. Saudi Arabia and Russia have committed to maintaining voluntary cuts of 2.2 million bpd until at least November 2024, with the potential for further extensions into 2025.
U.S. oil production, while still contributing to global supply, is showing signs of slowing. Growth projections for U.S. oil output have been revised down to 280,000 bpd for 2024, driven by a decline in the Bakken region and modest growth in the Permian Basin. This comes alongside disruptions in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico, where Hurricane Francine is expected to have caused a loss of 1.8 million barrels of production over two days.
Market Sentiment and Price Volatility: Hedge Funds and Speculators Dominate
Oil markets have seen significant price volatility in recent weeks, driven not by fundamental supply and demand shifts, but by speculative trading. According to Standard Chartered Bank, hedge funds and money managers have driven prices down to their most bearish levels since the 2008 financial crisis. This negative sentiment has been exacerbated by fears of a supply glut in 2025 and algorithm-driven trading strategies, which have created a feedback loop of declining prices.
Despite these speculative pressures, analysts from J.P. Morgan maintain that the global crude market is tight, with inventories below five-year averages. Global crude stocks, now at 4.42 billion barrels, are the lowest on record since 2017, while oil stocks at Cushing, Oklahoma, are severely depleted. J.P. Morgan’s pricing model suggests that Brent crude’s fair value should be $82 per barrel, $10 higher than current spot prices.
OPEC+ Production Strategy: Will it Stabilize Prices?
OPEC+ remains a critical player in balancing the oil market. The group’s decision to prolong supply cuts into November 2024, alongside plans to gradually restore 2.2 million bpd of idle capacity by December 2025, aims to stabilize prices. While this strategy has kept Brent crude around the $70 mark, analysts warn that OPEC+ may face challenges in the coming year as it navigates potential supply-demand imbalances.
Key producers like Iraq are expected to play a significant role in shaping market dynamics. The continued commitment of OPEC+ members to production cuts is essential in preventing a supply glut, particularly as global demand weakens.
U.S. Federal Reserve's Interest Rate Cuts: Impact on Oil Prices
The U.S. Federal Reserve’s expected interest rate cuts are likely to influence oil prices by boosting liquidity in the market. Lower rates reduce borrowing costs, which could support higher oil demand as economic activity increases. However, the extent of this impact remains uncertain, especially as traders await the Fed’s final decision on the size of the rate cut.
India's Expanding Refining Capacity and Energy Transition Plans
India’s petroleum consumption continues to grow in line with its ambitious economic and industrial expansion. The country plans to expand its refining capacity by 1.12 million bpd annually until 2028, a move that underscores its position as a key driver of global oil demand. At present, India’s refining capacity stands at 5.8 million bpd, and this figure is expected to rise by 22% over the next five years.
In parallel with its oil demand growth, India is also heavily investing in renewable energy. The country has set an ambitious target of achieving 500 gigawatts of renewable capacity by 2030, a significant increase from its current 153 GW. Banks have pledged $386 billion in investment commitments to help India transition to greener energy sources.
Tight Crude Supply and Inventory Draws: A Looming Concern
Despite concerns over weak demand, crude supply is expected to remain tight through the end of 2024. Rystad Energy projects that global liquids and crude balances will experience further stock draws as supply constraints persist. Notably, OPEC+ cuts, along with disruptions in Libya and reduced U.S. output, are key factors driving the tight supply situation.
The forecast for crude oil production in 2024 suggests a decline of 220,000 bpd, with OPEC+ cuts and Libyan production disruptions contributing to this shortfall. However, the situation may improve slightly as Brazil’s output is projected to recover in the second half of the year, and Nigeria’s production continues to grow.
Russia’s Oil Revenues Plummet Amid Price Drops
Russia’s oil export revenues have taken a significant hit, declining by nearly 30% since June 2024. Despite increasing export volumes, the value of Russian crude has dropped sharply as Brent prices fell to the low $70s. Russia’s flagship Urals crude is now trading below the $60 per barrel price cap, limiting the country’s ability to generate higher revenues despite increased shipments.
With seaborne crude exports averaging 3.21 million bpd in September 2024, the plunge in oil prices has diminished Russia’s weekly oil revenues to approximately $1.5 billion, the lowest level since February.
Conclusion: Oil Market Outlook for 2024
The global oil market faces a complex and challenging environment in 2024, characterized by tight supply, speculative trading, and geopolitical uncertainties. India’s growing role as a key oil importer, OPEC+ production strategies, and the influence of U.S. monetary policy will be critical factors in shaping the market's direction.
While supply remains constrained in the near term, concerns about a potential glut in 2025 loom large. The combination of tighter inventories, OPEC+ cuts, and potential disruptions from geopolitical events may provide support to prices.
That's TradingNEWS
Read More
-
IVV ETF Price Forecast: Is $684 Still Worth Paying For S&P 500 Exposure?
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveStocks
-
XRP ETF Rally: XRPI at $8.09 and XRPR at $11.60 as XRP-USD Rebounds Toward $1.47
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCrypto
-
Natural Gas Futures Price Holds Around $3.20 as Storage Tightens and Winter Premium Fades
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCommodities
-
USD/JPY Price Forecast: Yen Strength Turns 152 into a Make-or-Break Level
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveForex