Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) Stock: Is This 30% Drop a Prime Buying Opportunity?
Backed by AI Growth and Government Funding, Intel's Recent Decline Could Signal a Strong Buy Opportunity Intel's AI Expansion and Government Support Create a Golden Buying Opportunity with a 24% Upside Potential | That's TradingNEWS
Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) Stock Analysis: Is This a Buying Opportunity After the Steep Decline?
Stock Symbol: NASDAQ: INTC
Intel Corporation (NASDAQ: INTC) has had a tumultuous 2024, with its stock price dropping nearly 30% since July, currently trading around $28. Given its position in the semiconductor industry, this sharp decline has raised concerns among investors. However, for those willing to look deeper, the downturn presents a potential buying opportunity driven by the company’s long-term growth prospects in artificial intelligence (AI), data centers, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Intel's Stock Performance in 2024
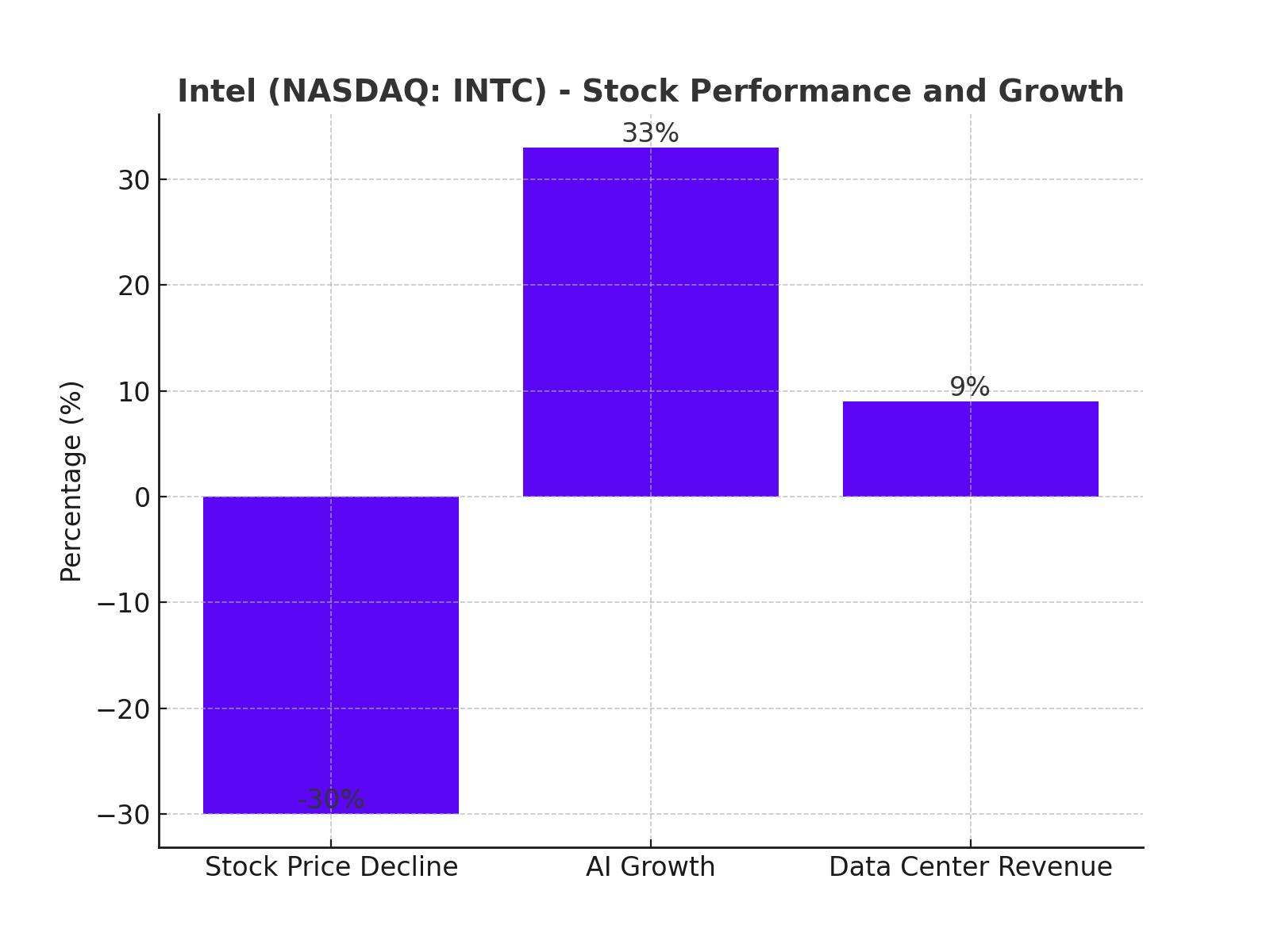
As of now, Intel’s stock price is hovering around $28 per share, representing a substantial 55% decline year-to-date (YTD). This level of volatility is driven by fluctuating financial results. Intel's quarterly earnings have consistently missed expectations, driven by a combination of declining revenues, unpredictable earnings per share (EPS), and macroeconomic factors affecting the semiconductor sector. Despite this, Intel's future is shaped by strategic investments and government support, making the case for potential future gains.
The stock's recent dip offers a contrasting view, with many investors seeing this as an entry point for a company that has robust R&D investments and is a beneficiary of government funding under the CHIPS Act. The significant financial support Intel has received through the CHIPS Act helps the company solidify its role as a leader in the semiconductor industry, especially as it works to bring state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities online in the U.S. and Europe.
Intel’s Ambitious Roadmap: The IDM 2.0 Strategy
The key to Intel's turnaround is its IDM 2.0 strategy, an ambitious plan aimed at reclaiming its leadership in semiconductor manufacturing by 2025. At the heart of this strategy is Intel's goal to roll out five advanced semiconductor nodes within four years, a feat the company has dubbed "five nodes in four years" (5N4Y). This roadmap is expected to enhance Intel's technological edge, particularly in high-performance computing and AI.
This push is reflected in Intel’s R&D expenditures. For instance, Intel has invested heavily in AI processors, data center chips, and edge computing. Compared to rivals like NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA) and AMD (NASDAQ: AMD), Intel's R&D budget is not only competitive but in some cases surpasses them. Intel is also targeting a larger share of the AI market, banking on its new AI-powered processors to gain a foothold in a market that is expected to grow exponentially over the next decade.
AI and Custom Chips: Key Drivers for Intel’s Growth
Intel’s position in AI should not be underestimated, especially with the increasing demand for AI-powered chips and custom processors. The company’s recent collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to develop custom AI chips underscores its commitment to expanding its AI footprint. The introduction of Intel Core Ultra processors, featuring advanced AI acceleration capabilities, positions Intel to capture a substantial share of the AI chip market. In addition, Intel recently launched its Xeon 6 Processor and Gaudi 3 AI Accelerator, designed for high-density workloads, making it clear that Intel is serious about competing in the AI space.
This diversification into AI hardware is crucial, as the demand for AI chips is expected to skyrocket, especially in data centers. AI workloads require immense computational power, and Intel is positioning itself as a key player in this space.
Financials: Revenue Growth and Profitability Concerns
Despite the promise of Intel’s R&D efforts, the company has struggled financially in 2024. Intel reported Q2 2024 revenues of $12.83 billion, falling short of the $12.94 billion consensus estimate. Net income for Q2 also posted a loss of $1.61 billion, or $0.38 per share, another significant miss compared to market expectations.
However, Intel’s Client Computing segment performed relatively well, with revenues hitting $7.41 billion, reflecting a 9% year-over-year growth, close to analysts’ expectations. Yet, the most concerning headlines came when Intel announced a workforce reduction of over 15% and the suspension of its attractive dividend in Q4 2024. This has led to a broad sell-off in the stock, causing prices to fall to $18.51 in mid-September.
On the bright side, analysts project a recovery in Intel's earnings by 2025, with a significant uptick expected as the company’s AI and data center products begin to ramp up. The company is also expected to return to profitability as its aggressive restructuring and cost-cutting measures take hold.
Technicals: Oversold and Poised for a Rebound?
From a technical perspective, Intel stock appears to be oversold. The stock is currently trading significantly below its 200-day moving average, a technical signal that often precedes a bullish reversal. In addition, the company’s price-to-book (P/B) ratio is 0.827x, which is historically low for Intel and suggests that the stock is trading below the value of its tangible assets.
According to historical price data, Intel has rarely traded at such a steep discount to its book value. This divergence from its long-term trend may suggest that the stock is poised for a rebound, especially if Intel can demonstrate progress in its turnaround strategy.
Valuation and Intrinsic Value
To assess the stock’s true value, we can look at a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, which helps estimate the intrinsic value of Intel’s shares. Using a discount rate of 8.54% and projecting a gradual improvement in revenue and free cash flow margins over the next five years, Intel’s intrinsic value per share is estimated to be around $28, which implies a 24% upside from its current level. This suggests that the market may be underestimating Intel’s long-term potential.
Moreover, Intel’s current price-to-book (P/B) ratio is much lower than its competitors. For comparison, AMD (NASDAQ: AMD) and NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA) are trading at price-to-book ratios of 4.6x and 7x, respectively. This massive valuation discrepancy suggests that Intel may be significantly undervalued relative to its peers.
Future Outlook: AI, Foundry Business, and CHIPS Act Support
Intel’s future growth largely hinges on its ability to capitalize on AI demand and the success of its foundry business. Intel has set ambitious goals for its Intel Foundry Services (IFS) division, aiming to become the second-largest foundry by 2030, with $15 billion in revenue. While this may not be an immediate catalyst, it represents a long-term growth driver for the company.
In addition, the CHIPS Act provides Intel with a significant competitive advantage. The billions in government funding Intel has received will help it build state-of-the-art semiconductor facilities, further enhancing its position in the global semiconductor supply chain. This should provide Intel with more control over its production, reducing reliance on external manufacturers like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC).
Risks and Challenges
While Intel's turnaround story is compelling, it is not without risks. The company’s heavy debt burden and leveraged balance sheet are causes for concern. Intel's significant capital expenditures, necessary for building out its foundry and AI businesses, could strain the company’s cash flow in the short term.
Furthermore, Intel’s competition is fierce. Companies like NVIDIA and AMD have firmly established themselves in the AI and data center markets, and Intel will need to innovate rapidly to catch up. Additionally, the global semiconductor industry is highly cyclical, and any economic downturn could further hurt demand for Intel's products.
Is Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) a Buy?
Given Intel’s current price levels, its growth prospects in AI, and its strong governmental backing through the CHIPS Act, Intel presents an attractive buying opportunity for long-term investors. The stock’s current valuation, well below book value, combined with the potential upside from its AI and foundry businesses, suggests that Intel may be significantly undervalued.
For those willing to tolerate near-term volatility, Intel’s long-term prospects remain bright, and the stock appears to offer a favorable risk-reward ratio at current levels. The potential for a 24% upside based on the intrinsic value calculation, coupled with strong AI and semiconductor demand, makes Intel a Strong Buy at current price levels.
For real-time updates on Intel’s stock price, check out the Intel chart here.
That's TradingNEWS
Read More
-
SCHD ETF Holds Ground With 3.6% Yield as Dividend Investors Eye Stability Over Growth
15.10.2025 · TradingNEWS ArchiveStocks
-
Ripple XRP (XRP-USD) Steadies at $2.43- SEC Shutdown Freezes ETF Decisions, Inflows Hit $61.6M
15.10.2025 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCrypto
-
NG=F Falls to $2.99 as Record Supply Outpaces Demand Despite 16.9 Bcf/d LNG Exports
15.10.2025 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCommodities
-
USD/JPY Price Forecast - Yen Weakens to 151.30 Amid Dollar Selloff
15.10.2025 · TradingNEWS ArchiveForex