Oil Market Dynamics: Navigating Uncertainty and Potential Triggers for Price Movements
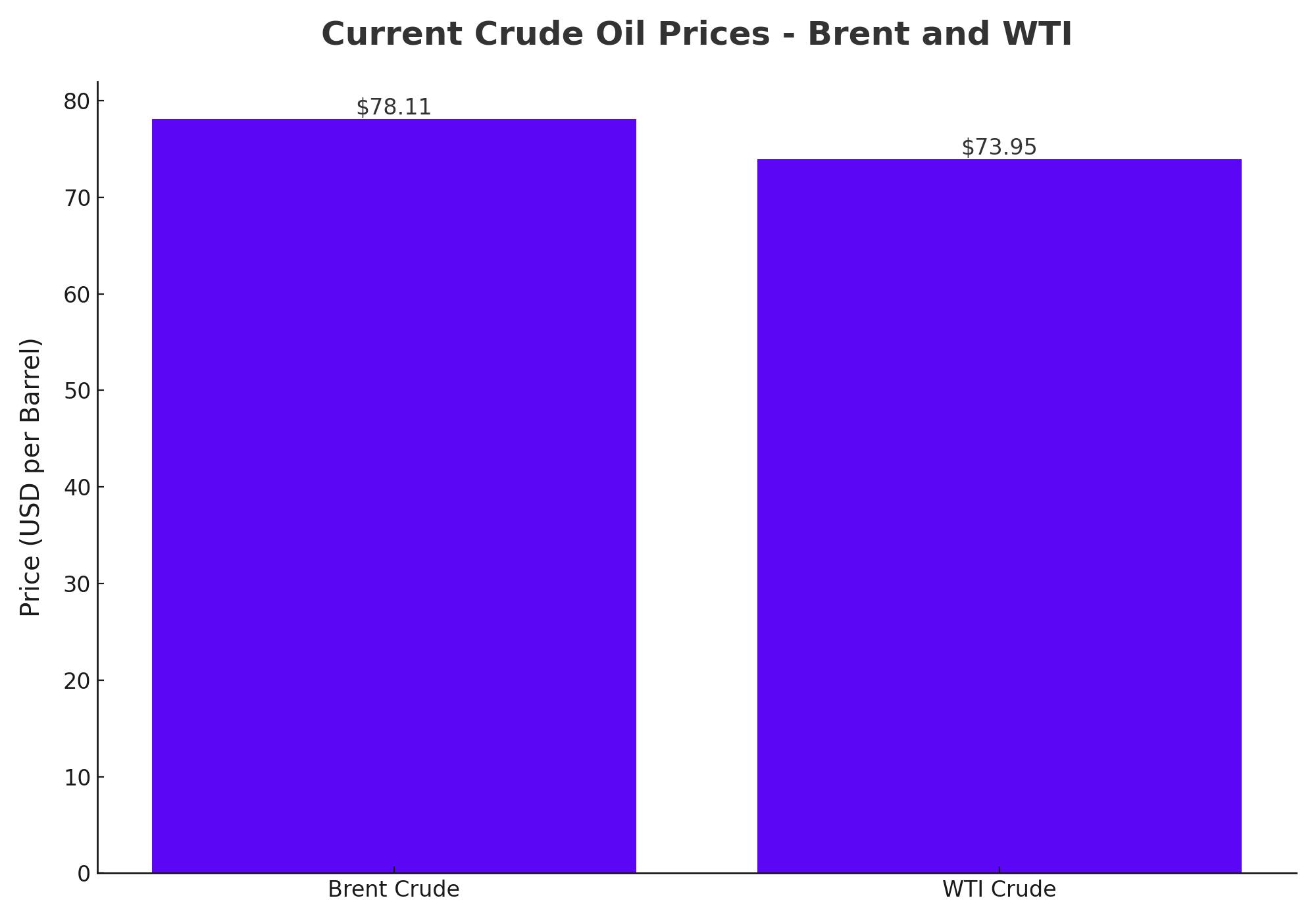
Crude oil prices have recently experienced notable fluctuations, influenced by a combination of geopolitical tensions, market fundamentals, and broader economic indicators. As of today, Brent crude has recovered to just over $80 per barrel, while West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is trading above $77 per barrel. This rebound comes after a dip earlier in the week, driven by a mix of bearish factors and renewed investor sentiment.
Geopolitical Tensions in the Middle East
The most significant driver of recent price volatility has been the escalating geopolitical tensions in the Middle East. The region's stability remains a critical factor for global oil supply, and any potential disruption could lead to a sharp increase in prices. Recent concerns stem from Iran's vow to retaliate against Israel following the assassination of a Hamas leader in Tehran. Although Iran has yet to act, the uncertainty surrounding its potential response has kept markets on edge. This has led to increased options trading activity as market participants seek protection against potential price spikes.
Inventory Data and Market Sentiment
Adding to the complexity, the latest data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) showed an unexpected crude oil inventory build for the week ending August 9. This surprised the market, as many were expecting a drawdown. However, the data also revealed declines in fuel inventories, suggesting that demand for refined products remains healthy. Despite this, the inventory build has added to the bearish sentiment, particularly when combined with reports of reduced refinery output and lower crude imports in China, the world's largest oil importer.
China's apparent weakening demand has been a growing concern. The country reported a 6.1% year-over-year decrease in refinery output for July, marking the fourth consecutive monthly decline. Additionally, imports of crude oil hit their lowest level since September 2022. The slowdown in demand is attributed to several factors, including the greater adoption of LNG-powered trucks, increased use of high-speed rail, and rising sales of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids.
Rate Cut Speculations and Economic Indicators
On the macroeconomic front, the possibility of a U.S. rate cut before the end of the year has also influenced oil prices. The release of consumer inflation data for July showed a modest increase in prices, which some market participants interpreted as supportive of a future rate cut by the Federal Reserve. Lower interest rates generally reduce the cost of borrowing, which can stimulate economic activity and increase demand for oil.
However, the market remains cautious, as these economic indicators are far from decisive, and the Federal Reserve's actions will depend on a broader set of economic data in the coming months.
Russian Export Routes and Strategic Maneuvers
Another critical factor in the current oil market dynamics is Russia's strategic adjustments in its export routes. In July, Russian petroleum product exports to Asia via the Cape of Good Hope reached an all-time high of 1.1 million metric tons. This shift to longer routes, bypassing the Suez Canal, is a response to security concerns in the Red Sea, where Iran-aligned Houthi forces have targeted vessels. Although Russia is not directly targeted by these attacks, the decision to avoid the Red Sea route highlights the increasing complexity of global oil logistics and the potential risks to supply.
Norway’s Offshore Investments and Future Supply Prospects
In the broader context of global oil supply, Norway's recent data showing a record high in offshore oil and gas investments is noteworthy. Total investments are estimated to reach $24 billion in 2024, a 4.1% increase from previous estimates. This investment surge is primarily driven by higher costs in production drilling and field developments. Norway, as Western Europe's top hydrocarbon producer, plays a crucial role in the region's energy supply, and its investment plans signal a commitment to maintaining production levels despite the challenges posed by high costs and environmental considerations.
China’s Industrial Output and Global Demand Implications
China's manufacturing and refinery output data further complicate the global oil demand outlook. While factory output grew by 5.1% in July, it fell short of analysts' expectations, raising concerns about the overall strength of the Chinese economy. As the world's largest oil importer, any slowdown in China's industrial activity has significant implications for global oil demand. The recent data suggests that demand may remain subdued in the near term, adding another layer of uncertainty to the market.
Texas’ Response to ESG Policies and Market Impacts
In the United States, Texas has taken a firm stance against financial institutions perceived as boycotting the energy industry. The recent addition of NatWest to Texas’ list of energy boycotters, due to its policy of phasing out financing for oil and gas projects, underscores the ongoing tension between the state’s energy policies and broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) trends. This move may influence the availability of financing for oil and gas projects in Texas, potentially impacting future production levels and market dynamics.
Outlook: Navigating a Complex Landscape
As the oil market navigates these intersecting factors, the future direction of prices will likely depend on a combination of geopolitical developments, economic indicators, and industry-specific trends. The potential for further price increases remains if geopolitical tensions escalate or if economic conditions improve, supporting higher demand. Conversely, any resolution to the tensions in the Middle East, a sustained slowdown in China's economy, or unexpected changes in global production levels could exert downward pressure on prices. Investors and industry stakeholders will need to stay vigilant, as the market remains poised for potential volatility in the months ahead.