U.S. Inflation Climbs to 3.5% in March 2024: A Sectors Breakdown
Analyzing the sharp rise in transportation and steady food costs, alongside energy fluctuations—implications for consumers and policymakers | That's TradingNEWS
In-Depth Analysis of U.S. Inflation Dynamics as of March 2024
Economic Overview
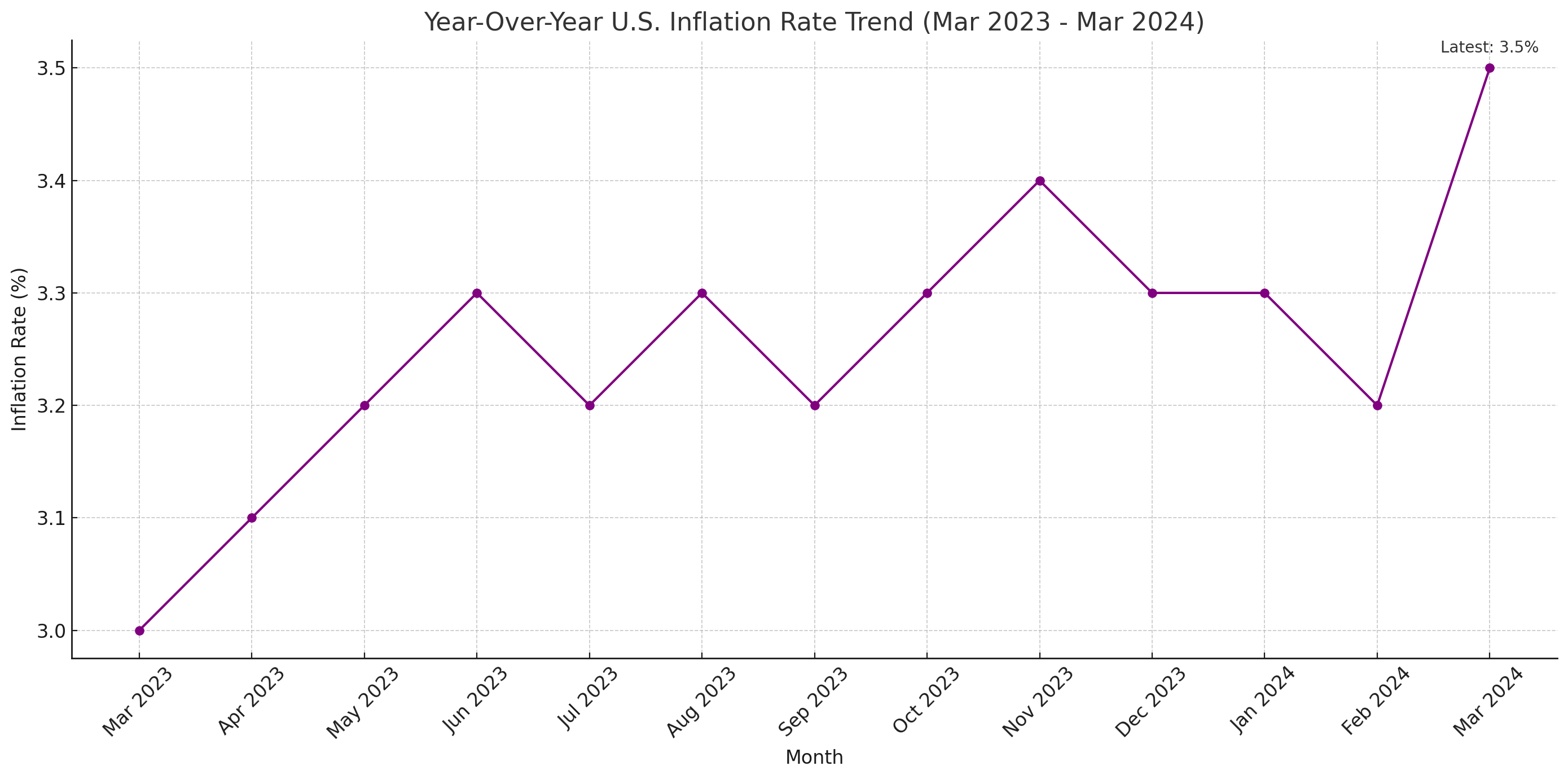
The inflation rate in the United States escalated to 3.5% year-over-year in March 2024, marking the highest rate since September of the previous year. This uptick from February's 3.2% surpassed the anticipated forecast of 3.4%, indicating a persistent upward pressure on prices across various sectors of the economy.
Sector-Specific Inflation Trends
Energy Sector
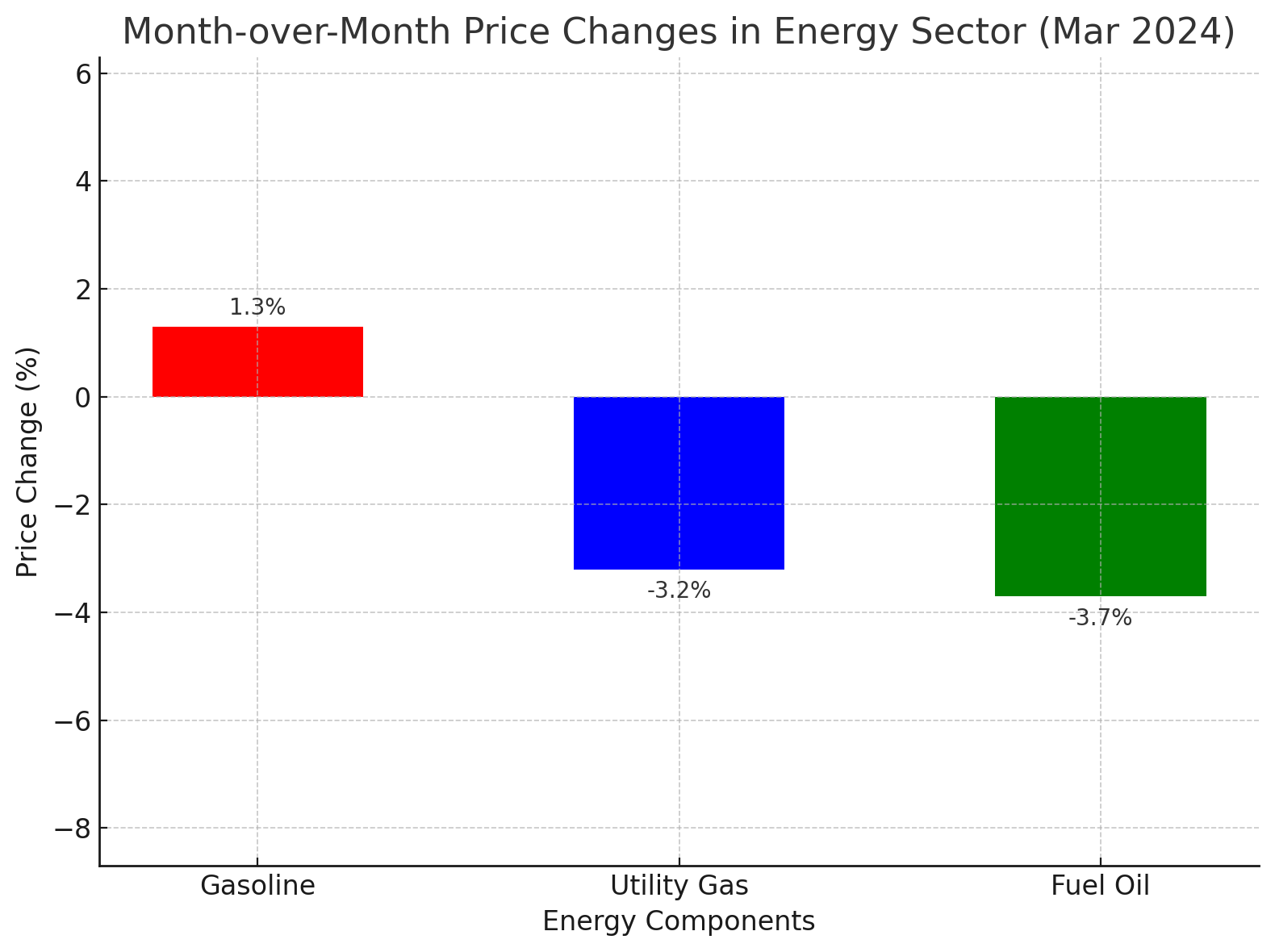
The energy sector experienced a notable rebound, with overall energy costs rising by 2.1% after a decline of 1.9% in February. This increase was led by gasoline prices, which rose by 1.3%, a stark contrast to the previous month's drop of 3.9%. However, not all components of the energy sector saw increases; utility gas service prices fell by 3.2%, and fuel oil prices decreased by 3.7%, though both declined less steeply than in February.
Food and Shelter
Food inflation remained stable at 2.2%, showing no change from the previous month, reflecting steady food prices amidst fluctuating market conditions. Shelter costs, a significant component of the CPI, continued to rise at a rate of 5.7%, mirroring the figures from the previous month, underscoring ongoing robustness in the housing market.
Transportation and Apparel
Transportation costs saw a sharp increase of 10.7%, up from 9.9% in February, highlighting rising costs in this vital economic sector. Conversely, apparel inflation was minimal, ticking up only 0.4% compared to no change previously.
Automobiles
The automotive sector presented a mixed picture, with new vehicle prices slightly decreasing by 0.1%, and used cars and trucks prices declining more significantly by 2.2%.
Core Inflation Analysis
Core inflation, which excludes the volatile food and energy sectors, remained steady at 3.8% annually, aligning with the previous month and slightly exceeding expectations of 3.7%. Monthly core inflation also held constant at 0.4%, defying expectations of a slowdown to 0.3%.
Inflation Metrics and Indices
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) increased by 0.4% on a month-over-month basis, consistent with the rate observed in February and above the forecasted 0.3%. The shelter and gasoline indices were significant contributors to this monthly rise. Noteworthy metrics include:
- CPI Median: Increased slightly to 4.55%
- CPI Trimmed-Mean: Rose to 3.61% from 3.51%
- Core Consumer Prices: Advanced to 316.70 points from 315.57
Export and Import Prices
March 2024 saw export prices at 149.00 points and import prices at 140.40 points, indicating slight increases from the previous month and reflecting broader economic interactions.
Consumer Expectations and Federal Reserve Outlook
Consumer inflation expectations remained steady at 3.00%. The steady core inflation and unexpected upticks in headline inflation rates complicate the Federal Reserve's interest rate strategy, potentially delaying anticipated rate cuts.
Impact on Monetary Policy
Given the current inflation dynamics, including higher-than-expected headline inflation and stable core inflation, the Federal Reserve faces challenges in balancing growth with inflation control. The likelihood of interest rate adjustments remains a pivotal topic, with market anticipations leaning towards a postponement in rate cuts.
Market Reactions and Future Projections
The persistence of inflationary pressures, particularly in the energy and shelter sectors, continues to influence financial markets and economic forecasts. The upcoming months will be critical in determining the trajectory of monetary policy adjustments and their timing.
Conclusion
As the U.S. grapples with varied inflation dynamics, the balance between economic growth and inflation control remains delicate. Market participants and policymakers must navigate these complexities with informed strategies, considering both current economic indicators and forward-looking projections. The inflation rate of 3.5% in March 2024 signals caution but also highlights the resilience of certain sectors, suggesting targeted approaches in monetary policy may be necessary moving forward.
That's TradingNEWS
Read More
-
GPIQ ETF Price Forecast: Can a 10% Yield at $52 Survive the Next Nasdaq Selloff?
09.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveStocks
-
XRP ETF Price Forecast: XRPI at $8.32, XRPR at $11.86 as $44.95M Inflows Defy BTC and ETH Outflows
09.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCrypto
-
Natural Gas Futures Price Forecast: Will The $3.00 Floor Hold After The $7 Winter Spike?
09.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCommodities
-
Stock Market Today: Dow Back Under 50K While S&P 500 and Nasdaq Push Higher as Gold Reclaims $5,000
09.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveMarkets
-
USD/JPY Price Forecast: Can Bulls Clear 157.5 Without Triggering a 160 Intervention Line?
09.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveForex