Rising Orange Juice Prices Signal Lucrative Investment Opportunity Amidst Supply Shortages
Florida's Declining Production, Citrus Greening Pandemic, and Natural Disasters Drive Orange Juice Prices Up,
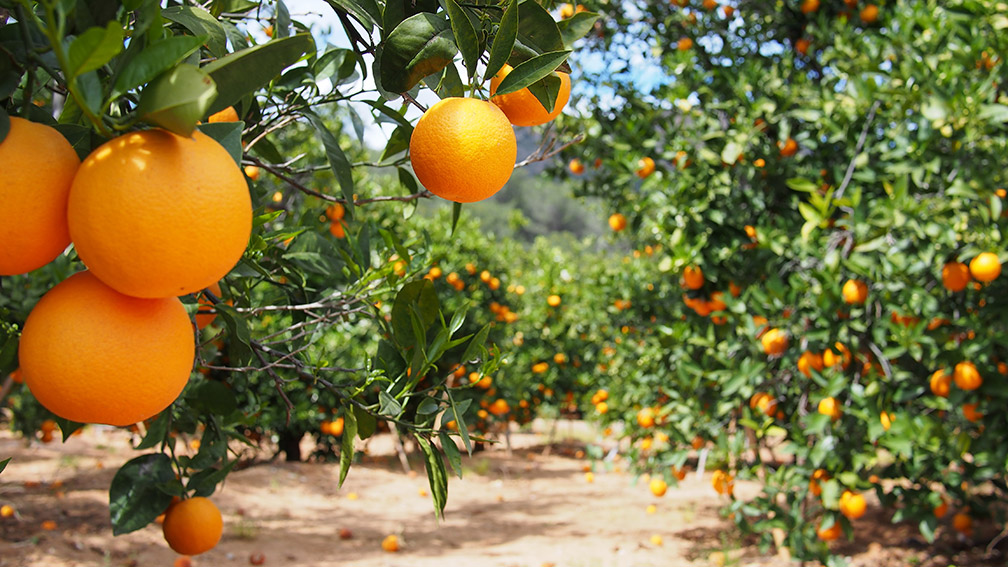
The breakfast table across America is feeling the financial crunch. Amidst a steep rise in the price of commodities, orange juice has joined the fray. Orange juice futures, contracts delineating the exchange of the citrus commodity, have almost doubled within a year, escalating from $1.40 to a staggering $2.60 per pound. The fallout is felt by consumers, as non-concentrated orange juice soared to $10 a gallon, while juice from concentrate has reached $6.27 per gallon. Evidently, the idiom, "as American as apple pie," might soon apply to orange juice prices as well.
In the Sunshine State of Florida, renowned as the heartland of orange production in the U.S, this surge in prices exposes a deeper, multifaceted crisis. Florida, producing the lion's share of American orange juice, is anticipated to generate only 16 million 90lb boxes of oranges this season. This forecast, by the U.S agriculture department, signals a stark 61% plunge from the previous season's production of 41 million boxes. The magnitude of this reduction appears more pronounced when compared with Florida's citrus heyday in the 1990s when it generated 200 million boxes annually. Matt Joyner, CEO of Florida Citrus Mutual, encapsulates this situation poignantly, acknowledging the disappointing crop size but emphasizing a determined resilience.
Simultaneously, Brazil, as the world's largest exporter of orange juice, seizes the opportunity to compensate for the dwindling output from Florida. Brazilian orange juice shipments have witnessed a significant 58% rise in the initial four months of the season, further contributing to the hike in prices. However, Florida's citrus sector, despite facing these tumultuous circumstances, continues to play a vital role in the state's economy. The University of Florida highlights that the citrus industry envelops 375,000 acres within the state, bolstering over 32,000 jobs, and brings in approximately $6.6bn each year.
The struggle of the Floridian citrus industry against climate phenomena, such as hurricanes, and the persistent citrus greening disease, also known as Huanglongbing, are key factors contributing to its current predicament. In 2022, Hurricane Ian devastated central Florida, severely impacting the state's citrus groves and causing approximately $1.07bn in damages to the agricultural sector, with $247m borne by citrus growers. Concurrently, the citrus greening pandemic, first identified in Florida in 2005, has continued unabated. This disease, spread by the Asian citrus psyllid, affects the tree's nutrient circulation and eventually results in the production of misshapen and bitter-tasting fruit, which are unsellable. As of 2015, nearly 90% of the trees were reportedly infected.
In response, Florida has invested substantial resources in research and development to combat citrus greening. Initiatives to replant old and infected trees have been ongoing, and the state is currently contemplating allocating $29m for protection and research within the citrus industry. Growers are also experimenting with nutritional supplements and trunk injections to strengthen trees against the disease. In parallel, researchers are striving to engineer citrus trees that demonstrate resistance to Huanglongbing.
Trading News Bellieves in Orange Juice
Investing in orange juice can be a lucrative opportunity due to several compelling factors:
Supply and demand dynamics: The rising price of orange juice can be attributed to falling production in the US state of Florida, which is a major producer. The US agriculture department predicts a significant 61% decline in production this season. As a result, Brazil, the largest orange juice exporter, has stepped in to fill the export gap, leading to price increases. This supply shortage coupled with high demand for orange juice poses an opportunity for investors.
Market potential and government reliance: Orange juice is a popular breakfast drink and a key source of Vitamin C for many people. Governments often rely on affordable orange juice to ensure their populations receive essential nutrients. The increasing price of orange juice becomes a concern for governments, highlighting the importance of maintaining the supply and affordability of this beverage.
Impacts of natural disasters: The citrus industry in Florida has been adversely affected by natural disasters, such as hurricanes, including Hurricane Ian. These events have caused significant damage and reduced production capacity, leading to a decline in the state's orange supply. Such disruptions can have long-term effects on the industry, creating potential opportunities for investors.
Disease and pest challenges: The citrus greening pandemic, caused by bacteria-infected insects, has affected orange trees in Florida, leading to unsellable fruit and tree deaths. This ongoing problem has further diminished Florida's orange supply. Additionally, the disease has spread to other regions, including California, potentially impacting orange production there as well. These challenges highlight the vulnerability of the orange industry and the potential for price increases in the future.
Shifts in production: California is expected to surpass Florida's orange production in the coming seasons, offering an alternative source for orange juice. However, the spread of citrus greening to California raises concerns about potential disruptions to their production. These shifts in production create opportunities for investors to monitor and capitalize on changes in the market.
Considering the combination of supply shortages, government reliance, natural disasters, disease challenges, and shifts in production, the price of orange juice could continue to rise. Investors can potentially benefit from this trend by exploring opportunities in the orange juice market. However, it is essential to conduct thorough research and consider market conditions before making any investment decisions.
Read More
-
IVV ETF Price Forecast: Is $684 Still Worth Paying For S&P 500 Exposure?
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveStocks
-
XRP ETF Rally: XRPI at $8.09 and XRPR at $11.60 as XRP-USD Rebounds Toward $1.47
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCrypto
-
Natural Gas Futures Price Holds Around $3.20 as Storage Tightens and Winter Premium Fades
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveCommodities
-
USD/JPY Price Forecast: Yen Strength Turns 152 into a Make-or-Break Level
14.02.2026 · TradingNEWS ArchiveForex